Pathophysiology of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Lesson by Drasti M Bhagat · 4 years ago ·
Toggle Collapse
Content Blocks
Word Breakdown
Benign: a growth that is not cancerous
Prostatic: affecting the prostate gland
Hyper: over/ more
Plasia: growth/ development
Hyperplasia: overgrowth of cells
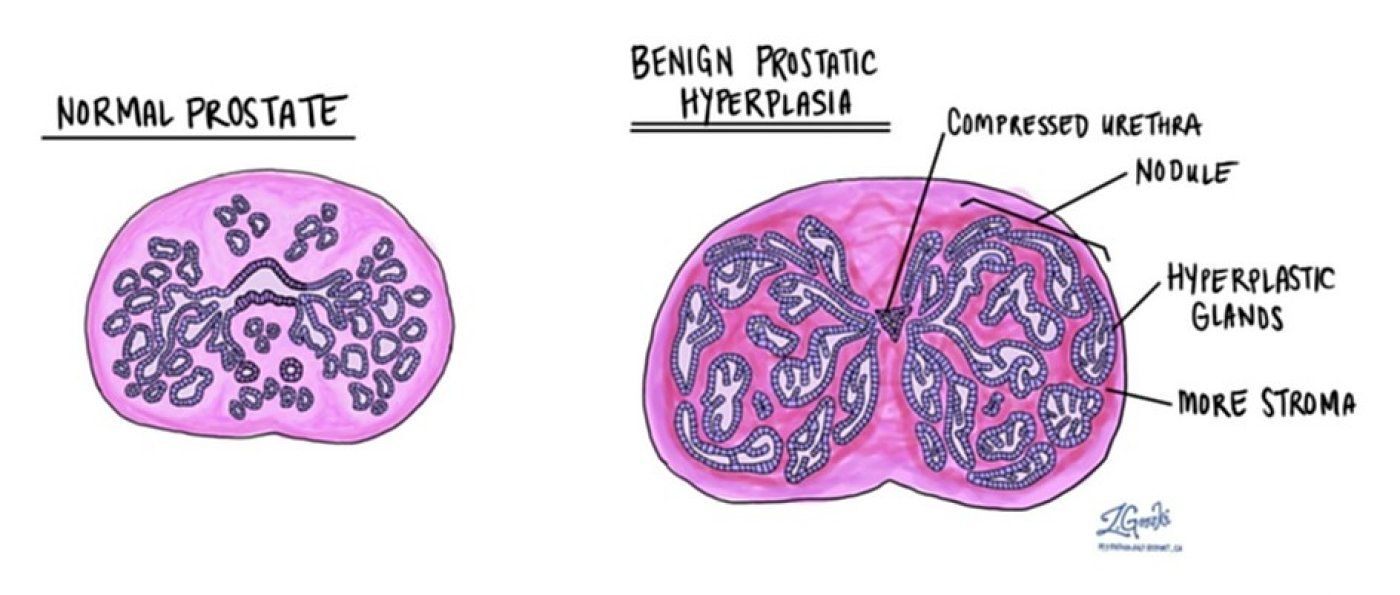
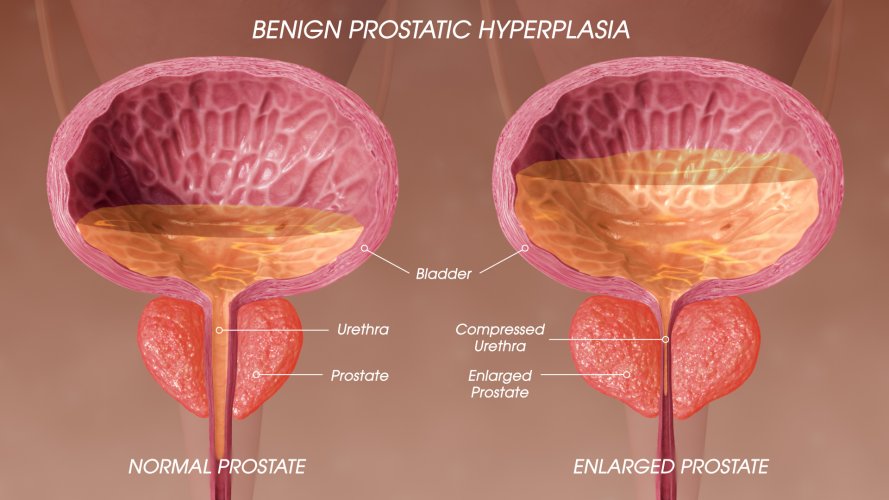
What happens? unregulated hyperplastic growth of the epithelial and fibromuscular tissues of the transition zone (TZ) and periurethral area. This blocks the flow of urine.
Pathophysiology
Genetics/ Hereditary
- loss of Y chromosome
- single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
Androgen
- testosterone derived play role in prostate health
- Androgen receptor expression may be upregulated
- incidence increases with age, when testosterone also decreases
Oestrogens
- men with metabolic dysfunction
- larger adipose tissue can lead to increased conversion of androgens to oestrogens
- along with the decrease in testosterone, the altered balance may account for the hyperplasia
Insulin
- increased incidence of BPH in diabetes pts
- the receptor for an insulin mediator is found in higher levels
Growth Factors
- changes in sex hormone balance maintain hyperplastic processes
- linked with inflammation?
https://bjui-journals-onlinelibrary-wiley-com.libaccess.senecacollege.c…
Collaborators
None listed.
License
Pathophysiology of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) by Drasti M Bhagat is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY), except where otherwise noted.


Comments
Be the first to comment!