1.2.2 Balance Sheet and Statement of Cash Flows
- Read more about 1.2.2 Balance Sheet and Statement of Cash Flows
- Log in or register to post comments
- 47 views
The Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is also called the statement of financial position.
The balance sheet reports a company’s financial position as at a specific date (e.g., last day of a monthly, quarterly, or annual reporting period). Since it is presented as at a specific date, you can think of the balance as a snapshot of the company’s financial position at a particular point in time.
Note: the other 3 statements cover a period of time.
From the balance sheet above, note the Accounting Equation (Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity):
Total Assets = $90,973 which equals the Total Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity = $90,973.
Balance Sheet Has Three Main Elements:
- Assets: Economic resources controlled by the entity as a result of past business events from which future economic benefits may be obtained.
- Current assets: Expected to be converted to cash, sold, or consumed during the next 12 months or within the business’ operating cycle, whichever is longer, and include:
- Cash and cash equivalents
- Short-term investments
- Accounts and notes receivable
- Inventory
- Prepaid expenses
- Non-current assets: Will be held longer than one year and include:
- Property and equipment
- Land
- Buildings
- Computers
- Equipment
- Intangibles
- Long-term investments
- Current assets: Expected to be converted to cash, sold, or consumed during the next 12 months or within the business’ operating cycle, whichever is longer, and include:
- Liabilities: Debts the entity owes as a result of a past event, and which it expects to pay off in the future using some of its assets.
- Current liabilities: Debts payable in the next 12 months or within the business’ operating cycle, whichever is longer, and include:
- Accounts payable
- Income taxes payable
- Accrued expenses payable
- Current maturities of long-term debt
- Non-current liabilities: Debts payable more than one year from the balance sheet date and include:
- Long-term notes payable
- Bonds payable
- Current liabilities: Debts payable in the next 12 months or within the business’ operating cycle, whichever is longer, and include:
- Shareholders’ equity: Owners’ remaining interest in the assets of the company after deducting all its liabilities (i.e., owners’ claim on the company’s assets net of company’s liabilities, hence, called net assets), consisting of two components:
- Share capital: capital (usually in the form of cash) received from its owners in exchange for shares of the company. Also called common shares.
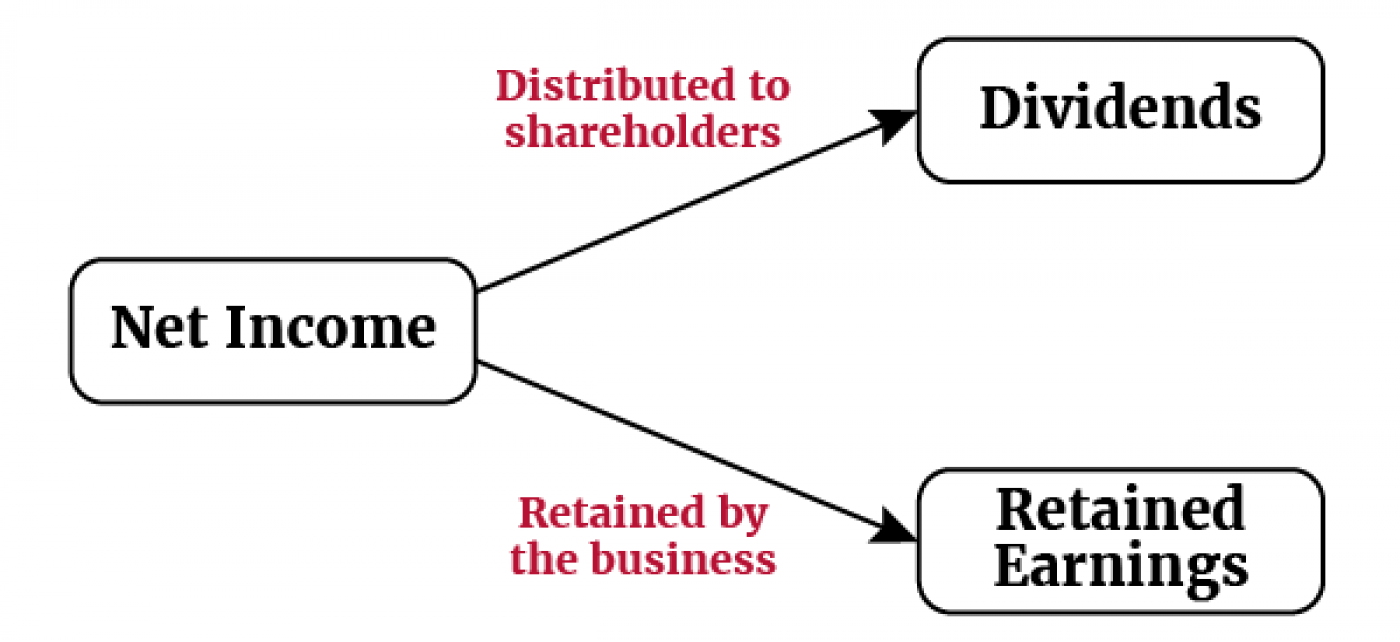
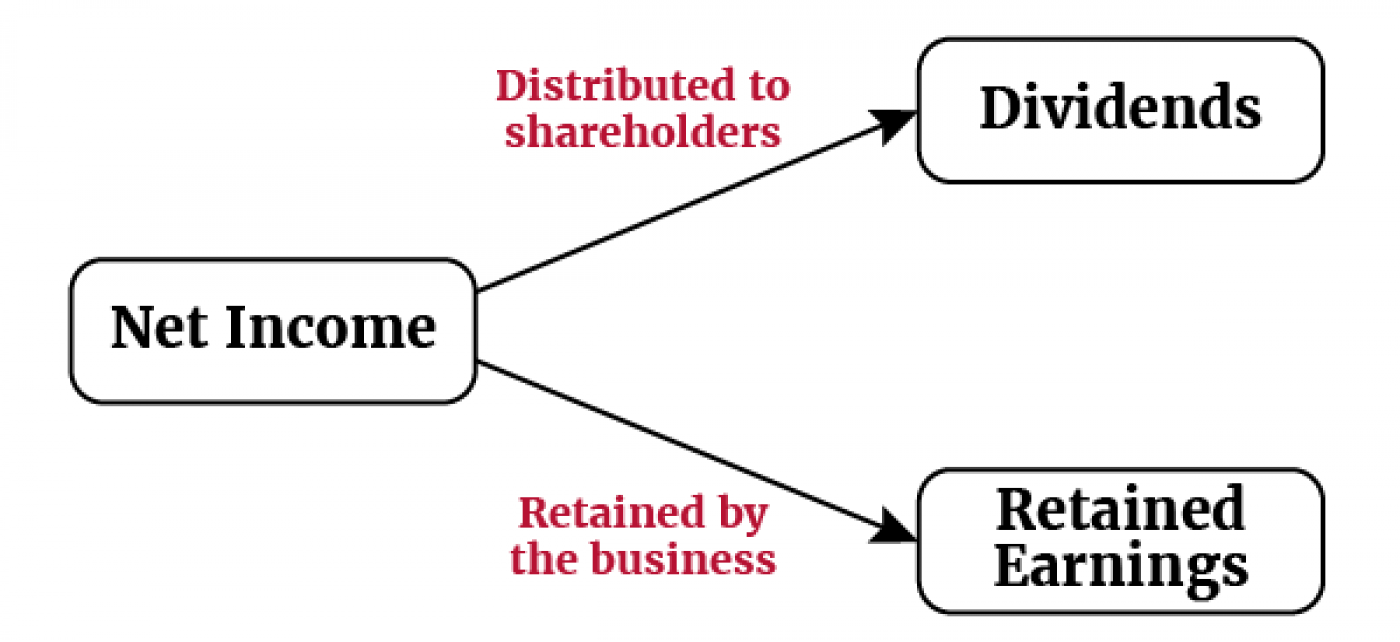
- Retained earnings: the cumulative net income earned by the company over its lifetime, less its cumulative net losses and dividends.
Note: a portion of net income is typically distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends and the remainder is retained by the business that is called retained earnings.
The balance sheet takes its name from the fact that the assets (A) must always equal (be in balance with) the sum of the liabilities (L) and the shareholders' equity (SE).
A = L + SE
(Assets) = (Liabilities) + (Shareholders' Equity)
Assets refer to the economic resources of the company.
Companies can finance the economic resources in two ways:
- Liabilities: Financing provided by creditors
- Shareholders' equity: Financing provided by shareholders
Typical Account Titles
| Assets | Liabilities | Shareholders’ Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Cash | Trade Payables | Share Capital (or Common Shares) |
| Short-Term Investment | Short-term Borrowing | Retained Earnings |
| Trade Receivable | Long-term Borrowing | |
| Notes Receivable | Provisions | |
| Inventory (to be sold) | Other Liabilities |

Login or register to share your adaptations.
List of adaptions
Be the first to add your adaptation here!
Login or register to engage in the review and feedback process.
Reviews and Feedback
Be the first to review!


Comments
Be the first to comment!